CUSP is seeking support for a bipartisan Congressional Aquaculture Caucus to:
1. Increase national food security
2. Provide healthy, nutritious seafood
3. Provide jobs in rural and coastal communities
4. Support economic development in struggling areas
Domestic Aquaculture – Room to Grow!
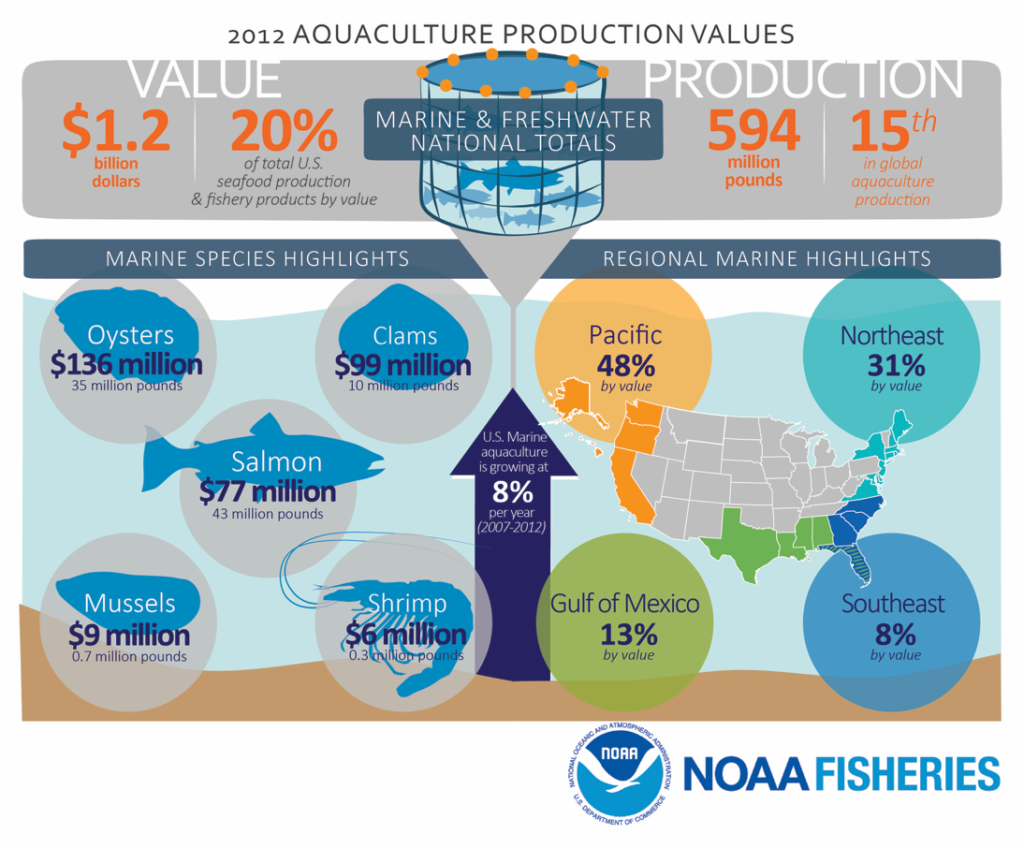
With the implementation of the Fishery Management Plan for Offshore Marine Aquaculture in the Gulf of Mexico, a regulatory framework is now established for aquaculture in federal waters.
Challenges to domestic aquaculture growth include an onerous and redundant permitting process, lack of investment, and lack of government support.
Economic Imperative:
- Globally, aquaculture is the world’s fastest growing food producing sector with an average annual growth rate of 8%.(1)
- Over half of the seafood consumed globally now comes from aquaculture.
- Global aquaculture production is worth over $100 billion. America produces only 1% of that total.
- The U.S. currently imports over 91% of its seafood, creating a trade deficit of $11 billion. America is the world’s largest importer of aquaculture products.
- Shellfish is the largest and fastest growing segment in the U.S., with oyster production doubling on the East Coast in the last five years to almost $500 million. (2)
- In the U.S. 75,000 to 100,000 direct and indirect jobs, from working waterfronts to the agricultural heartland, can be created with every 1 million metric tons produced from commercial aquaculture. (3)
Environmental Imperative:
- Another 40 million tons of seafood worldwide per year will be needed by 2030 just to meet current consumption rates. (1)
- Because all the world’s wild fisheries are at or near capacity, meeting increased demand will require increased production from aquaculture, either domestic or imported.
- The U.S. has over 38,610 square miles of federal waters that have suitable depth and currents to support offshore aquaculture.
- S. producers work with the EPA, NOAA, USDA, USFWS, ACOE and numerous state environmental agencies to ensure they maintain water quality, native fish stocks and environmental quality.
- Responsibly managed aquaculture has the least environmental impact of any other form of protein production. (4)
Health and Food Safety Imperative:
- The USDA, HHS and the American Heart Association recommends consumption of at least 8 ounces of seafood per week for optimum heart health benefits.
- Studies have shown fish consumption significantly lowers the risk of heart disease by 36%. (5)
- From 2005 to 2013, the FDA rejected nearly 18,000 shipments of imported seafood because they were unfit for human consumption. (6) Currently, the FDA has the manpower to inspect only 1% of all imported seafood shipments.
- Producing seafood domestically ensures a safe, secure supply of healthy protein.
Please contact us if you are interested in participating in this important effort to further communicate the importance of U.S. Aquaculture for economic development, food security, and job creation.
(1) United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) 2014
(2) East Coast Shellfish Growers Association
(3) NOAA 2008
(4) Blue Frontiers report, Conservation International 2011
(5) Mozaffarian and Rimm, Harvard School of Public Health 2006
(6) USDA Analysis of FDA Import Refusals Report 2016
